Question 1
The left describes OSI layers, while the right provides some terms. Drag the items on the right to the proper locations.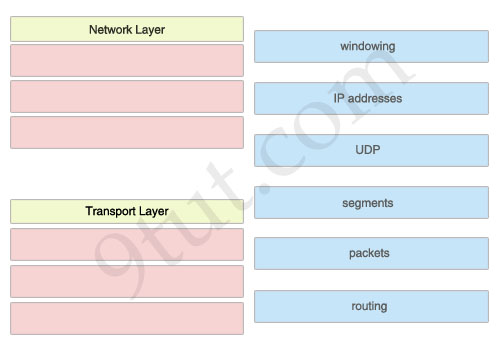
Answer:
Network Layer:1) IP addresses
2) packets
3) routing
Transport Layer:
1) windowing
2) UDP
3) segments
Question 2
The above describes some categories, while the below provides their corresponding router output lines. Drag the above items to the proper locations.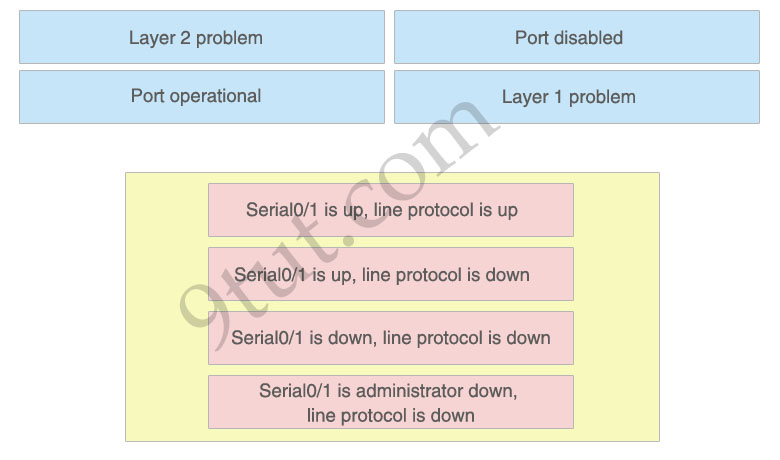
Answer:
1) Port operational: Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is up2) Layer 2 problem: Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down
3) Layer 1 problem: Serial0/1 is down, line protocol is down
4) Port disabled: Serial0/1 is administrator down, line protocol is down
Explanation:
A simple way to find out which layer is having problem is to remember this rule: “the first statement is for Layer 1, the last statement is for Layer 2 and if Layer 1 is down then surely Layer 2 will be down too”, so you have to check Layer 1 before checking Layer 2. For example, from the output “Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down” we know that it is a layer 2 problem because the first statement (Serial0/1 is up) is good while the last statement (line protocol is down) is bad. For the statement “Serial0/1 is down, line protocol is down”, both layers are down so the problem belongs to Layer 1.There is only one special case with the statement “…. is administrator down, line protocol is down”. In this case, we know that the port is currently disabled and shut down by the administrators.
Question 3
A user is unable to connect to the Internet. Based on the layered approach to troubleshooting and beginning with the lowest layer. Follow the guide and drag the contents to relevant modules.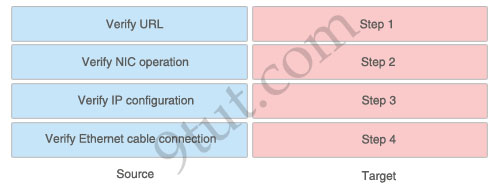
Answer:
1) Verify Ethernet cable connection: Step 12) Verify NIC operation: Step 2
3) Verify IP configuration: Step 3
4) Verify URL: Step 4
Explanation:
The question asks us to “begin with the lowest layer” so we have to begin with Layer 1: verify physical connection; in this case an Ethernet cable connection. For your information, “verify Ethernet cable connection” means that we check if the type of connection (crossover, straight-through, rollover…) is correct, the RJ45 headers are plugged in, the signal on the cable is acceptable…Next we “verify NIC operation”. We do this by simply making a ping to the loopback interface 127.0.0.1. If it works then the NIC card (layer 1,2) and TCP/IP stack (layer 3) are working properly.
Verify IP configuration belongs to layer 3. For example, checking if the IP can be assignable for host, the PC’s IP is in the same network with the gateway…
Verifying the URL by typing in your browser some popular websites like google.com, microsoft.com to assure that the far end server is not down (it sometimes make we think we can’t access to the Internet). We are using a URL so this step belongs to layer 7 of the OSI model.
Question 4
The left describes the types of cables, while the right describes the purposes of the cables. Drag the items on the left to the proper locations. (Not all items can be used).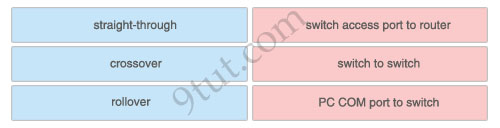
Answer:
1) straight-through: switch access port to router2) crossover: switch to switch
3) rollover: PC COM port to switch
Explanation:
To remember which type of cable you should use, follow these tips:- To connect two serial interfaces of 2 routers we use serial cable
– To specify when we use crossover cable or straight-through cable, we should remember:
Group 1: Router, Host, Server
Group 2: Hub, Switch
One device in group 1 + One device in group 2: use straight-through cable
Two devices in the same group: use crossover cable
For example: we use straight-through cable to connect switch to router, switch to host, hub to host, hub to server… and we use crossover cable to connect switch to switch, switch to hub, router to router, host to host… )
Question 5
The left describes the types of switch ports, while the right describes the features. Drag the options on the right to the proper locations.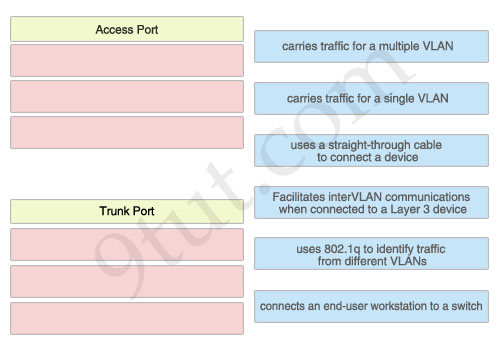
Answer:
Access Port:- Carries traffic for a single VLAN
– Uses a straight-through cable to connect a device
– Connects an end-user workstation to a switch
Trunk Port:
- Carries traffic for a multiple VLAN
– Uses 802.1q to identify traffic from different VLANs
– Facilitates interVLAN communications when connected to a Layer 3 device
Question 6
The above describes the Spanning-Tree Protocol port states, while the below describes their functions. Drag the above items to the proper locations.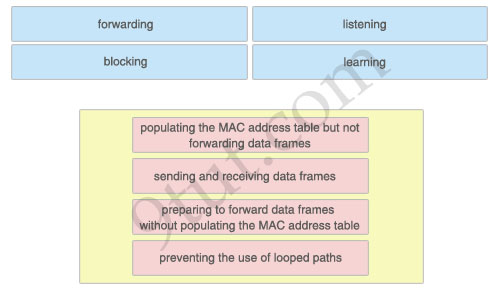
Answer:
- Learning: populating the MAC address table but not forwarding data frames – Forwarding: sending and receiving data frames
– Listening: preparing to forward data frames without populating the MAC address table
– Blocking: preventing the use of looped paths
No comments:
Post a Comment