Question 1
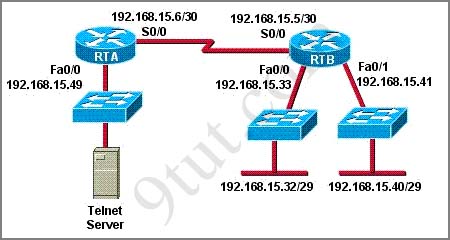
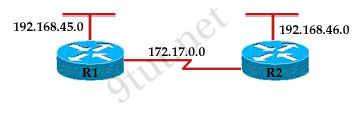
Refer to the exhibit. What will happen to HTTP traffic coming from the Internet that is destined for 172.16.12.10 if the traffic is processed by this ACL?| router#show access-lists Extended IP access list 110 10 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq telnet 20 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq smtp 30 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq http 40 permit tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any |
B. Traffic will be accepted per line 40 of the ACL.
C. Traffic will be dropped, because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL.
D. Traffic will be accepted, because the source address is not covered by the ACL.
Answer: C
Explanation
The syntax of an extended access list is:access-list access-list-number {permit | deny} protocol source {source-mask} destination {destination-mask} [eq destination-port]
Notice that in our access list, the network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 is specified as the source but the question asks about “HTTP traffic coming from the Internet that is destined for 172.16.12.10″, which means 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 is the destination network. So in this case there is no match in our access list and the traffic will be dropped because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL. It is surely a tricky question!
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes the effect that the Router1 configuration has on devices in the 172.16.16.0 subnet when they try to connect to SVR-A using Telnet or SSH?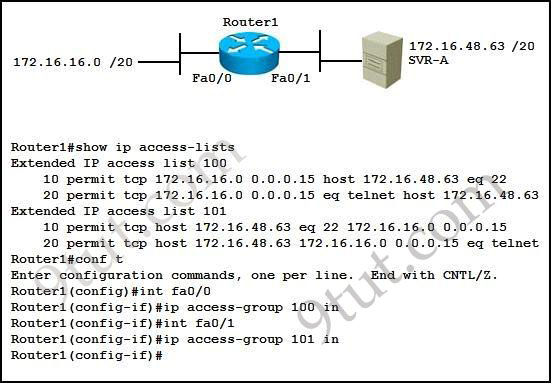
A. Devices will not be able to use Telnet or SSH.
B. Devices will be able to use SSH, but not Telnet.
C. Devices will be able to use Telnet, but not SSH.
D. Devices will be able to use Telnet and SSH.
Answer: B
Explanation
Let’s analyze the access list 100:+ 10 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 host 172.16.48.63 eq 22: allows TCP traffic from network 172.16.16.0/28 to access host 172.16.48.63 with a destination port of 22 (SSH)
+ 20 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet host 172.16.48.63: allows TCP traffic from network 172.16.16.0/28 with a source port of 23 (telnet) to access host 172.16.48.63
Notice that if a device wants to telnet (or SSH) to SVR-A server it must use the destination port of 23 (or 22), not a source port of 23 (or 22).
Access list 100 is applied on the inbound direction of Fa0/0 so it will only filter traffic from 172.16.16.0 subnet to the SVR-A server.
Access list 101 is very similar to access list 100 but it is applied on the inbound direction of Fa0/1 so it will filter traffic from SVR-A server to 172.16.16.0 subnet. In ACL 101:
+ 10 permit tcp host 172.16.48.63 eq 22 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15: allows TCP traffic from host 172.16.48.63 with a source port of 22 (SSH) to access network 172.16.16.0/28.
+ 20 permit tcp host 172.16.48.63 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet: allows TCP traffic from host 172.16.48.63 to access network 172.16.16.0/28 with a destination port of telnet.
Notice that the returned traffic from SVR-A to network 172.16.16.0/28 (resulting from telnet or SSH session) will have a source port of 23 (Telnet) or 22 (SSH)
In conclusion, the first statements of each ACL will allow devices to “SSH” to SVR-A. But they can’t telnet because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL.
In this question, the second statements of each ACL can be considered “wrong” if we intend to filter telnet or SSH traffic and they have no effect on the Telnet or SSH traffic.
Question 3
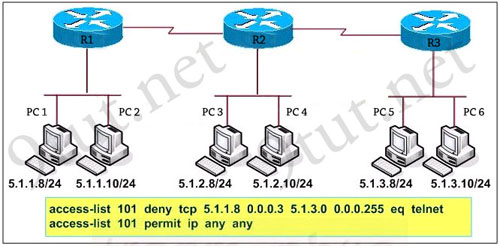
Refer to the exhibit. Which three variables (router, protocol port, and router ACL direction) apply to an extended ACL that will prevent student 01 from securely browsing the internet?
B. Router 3
C. HTTPS
D. IN
E. Router 1
Answer: B C D
Explanation
There are 3 routers we can place this access list: Router 1, Router Main and Router 3 but in theory, an extended access list should be placed close to the source -> Router 3 is the best choice -> B is correct.The traffic we need to filter here is “securely browsing the internet” so it is HTTPS -> C is correct.
Finally we should apply this access list to the inbound direction so that Router 3 will filter this traffic before making routing decision. It helps save processing resources on Router 3 -> D is correct.
Question 4
Which two statements apply to dynamic access lists? (choose two)A. they offer simpler management in large internetworks.
B. you can control logging messages.
C. they allow packets to be filtered based on upper-layer session information.
D. you can set a time-based security policy.
E. they provide a level of security against spoofing.
F. they are used to authenticate individual users.
Answer: A F
Explanation
Dynamic ACLs have the following security benefits over standard and static extended ACLs:+ Use of a challenge mechanism to authenticate individual users
+ Simplified management in large internetworks
+ In many cases, reduction of the amount of router processing that is required for ACLs
+ Reduction of the opportunity for network break-ins by network hackers
+ Creation of dynamic user access through a firewall, without compromising other configured security restrictions
(Reference: CCNA Exploration 4 – Dynamic ACLs)
Question 5
Which command shows if an access list is assigned to an interface?A. show ip interface [interface] access-lists
B. show ip access-lists interface [interface]
C. show ip interface [interface]
D. show ip access-lists [interface]
Answer: C
Explanation
The output of “show ip interface [interface]” command is shown below:
In the output we can see the access list 1 is applied to this interface on inbound direction.
Question 6
Which item represents the standard IP ACL?A. access-list 50 deny 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255
B. access-list 110 permit ip any any
C. access-list 2500 deny tcp any host 192.168.1.1 eq 22
D. access-list 101 deny tcp any host 192.168.1.1
Answer: A
Explanation
The standard access lists are ranged from 1 to 99 and from 1300 to 1999 so only access list 50 is a standard access list.Question 7
Which statement about access lists that are applied to an interface is true?A. you can apply only one access list on any interface
B. you can configure one access list, per direction, per layer 3 protocol
C. you can place as many access lists as you want on any interface
D. you can configure one access list, per direction, per layer 2 protocol
Answer: B
Explanation
We can have only 1 access list per protocol, per direction and per interface. It means:+ We can not have 2 inbound access lists on an interface
+ We can have 1 inbound and 1 outbound access list on an interface
Question 8
A network engineer wants to allow a temporary entry for a remote user with a specific username and password so that the user can access the entire network over the internet. Which ACL can be used?A. reflexive
B. extended
C. standard
D. dynamic
Answer: D
Explanation
We can use a dynamic access list to authenticate a remote user with a specific username and password. The authentication process is done by the router or a central access server such as a TACACS+ or RADIUS server. The configuration of dynamic ACL can be read here: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk583/tk822/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094524.shtmlQuestion 9
Which parameter standard access list takes into consideration for traffic filtering decisions?A. Source MAC address
B. Destination IP address
C. Destination MAC address
D. Source IP address
Answer: D
Question 10
In which solution is a router ACL used?A. protecting a server from unauthorized access
B. controlling path selection, based on the route metric
C. reducing router CPU utilization
D. filtering packets that are passing through a router
Answer: D