Question 1
Which three statements about RSTP are true? (choose three)A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconverging time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expends the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
E. RSTP use the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
F. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
Answer: A B F
Question 2
Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (choose two)A. blocking
B. learning
C. disabled
D. forwarding
E. listening
Answer: A D
Explanation
RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding but the answers don’t mention about discarding state so blocking state (answer A) may be considered the best alternative answer.Question 3
Which command enables RSTP on a switch?A. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
B. spanning-tree uplinkfast
C. spanning-tree backbonefast
D. spanning-tree mode mst
Answer: A
Question 4
At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops?A. data link
B. network
C. physical
D. transport
Answer: A
Question 5
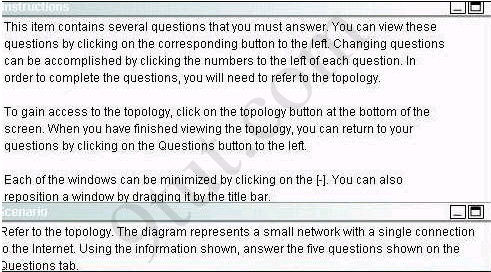
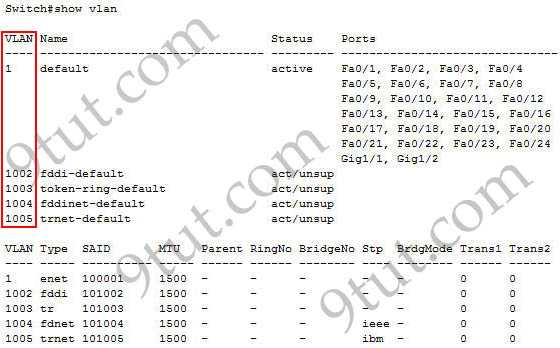
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output shown from this Cisco Catalyst 2950, what is the most likely reason that interface FastEthernet 0/10 is not the root port for VLAN 2?Switch# show spanning-tree interface fastethernet0/10

B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
Answer: C
Question 6
Which two of these statements regarding RSTP are correct? (Choose two)A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
B. RSTP defines new port roles.
C. RSTP defines no new port states.
D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Answer: B E
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)
B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: A B F
Explanation
The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.Because SwitchC is the root bridge so the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports -> B and F are correct.
Now we come to the most difficult part of this question: SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, “cost” is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
| Link speed | Cost |
| 10Mbps | 100 |
| 100Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
One more thing to notice is that a root bridge always advertises the cost to the root bridge (itself) with an initial value of 0.
Now let’s have a look at the topology again

Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.
Below summaries all the port roles of these switches:

+ RP: Root Port (forwarding state)
+ AP: Alternative Port (blocking state)
Question 8
Which two protocols are used by bridges and/or switches to prevent loops in a layer 2 network? (Choose two)A. 802.1d
B. VTP
C. 802.1q
D. STP
E. SAP
Answer: A D
Question 9
Which switch would STP choose to become the root bridge in the selection process?A. 32768: 11-22-33-44-55-66
B. 32768: 22-33-44-55-66-77
C. 32769: 11-22-33-44-55-65
D. 32769: 22-33-44-55-66-78
Answer: A
Question 10
Refer to the topology shown in the exhibit. Which ports will be STP designated ports if all the links are operating at the same bandwidth? (Choose three)
B. Switch A – Fa0/1
C. Switch B – Fa0/0
D. Switch B – Fa0/1
E. Switch C – Fa0/0
F. Switch C – Fa0/1
Answer: B C D
Explanation
First by comparing their MAC addresses we learn that switch B will be root bridge as it has lowest MAC. Therefore all of its ports are designated ports -> C & D are correct.On the link between switch A & switch C there must have one designated port and one non-designated (blocked) port. We can figure out which port is designated port by comparing their MAC address again. A has lower MAC so Fa0/1 of switch A will be designated port while Fa0/1 of switch C will be blocked -> B is correct.